Velocity Measurement Tool¶
The toolset allows to create kymograms and to measure the velocity of particles in the kymogram. The user can make a segmented line selection on the kymogram and the mean velocity for each segment will be measured. A synthetic example image can be found here: moving-particles-2.tif
Getting started¶
To install the tools, drag the link Velocity_Measurement_Tool.txt to the ImageJ launcher window, save it under macros/toolsets in the ImageJ installation and restart ImageJ.
Select the "Velocity Measurement Tool" toolset from the >> button of the ImageJ launcher.

- the *?*-button opens this help page
- the k-button creates a kymogram of the current image
- the v-button measures the velocities corresponding to the line or segmented line selection on the kymogram
The measurement of the velocities is a modified version of code from www.embl.de/emnet/html/kymograph.html (tsp050706.txt TimeSpacePlot (Kymograph)) by J. Rietdorf FMI Basel and A. Seitz EMBL Heidelberg.
Usage¶
Make a segmented line selection of the path of the particle for which you want to measure the velocity. You can use a z-projection (Image>Stacks>Z Project...) to create the selection and then transfer it to the time-series stack using ctrl+shift+e. Now press the k-button to get the kymogram. Now make a segmented line selection on the trace of the particle in the kymogram and press the v-button to get the speed measurements.
Results¶
| The input time series: | The kymogram: |
 |
 |
The kymogram with a segmented line selection:

The measurements in the results table:
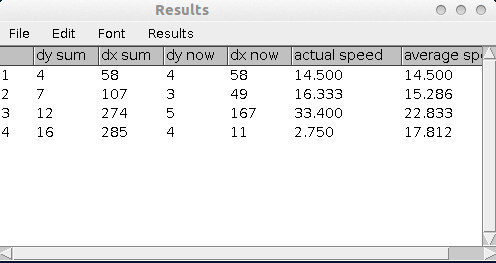
- dy sum - the sum of the distance travelled in y direction
- dx sum - the sum of the distance travelled in x direction
- dy now - the distance travelled on the current path segment in y direction
- dx now - the distance travelled on the current path segment in x direction
- actual speed - the speed on the current path segment
- average speed - the average speed upto and including the current path segment
The x-axis represents the distance and the y-axis represents the time in the units set for the image for example pixel/time unit or micron/second.
Publications that use the tool¶
- Tsai, F.-C., Henderson, J.M., Jarin, Z., Kremneva, E., Senju, Y., Pernier, J., Mikhajlov, O., Manzi, J., Kogan, K., Le Clainche, C., et al. (2022). Activated I-BAR IRSp53 clustering controls the formation of VASP-actin–based membrane protrusions. Sci. Adv. 8, eabp8677. 10.1126/sciadv.abp8677.
- - Hahn, I., Voelzmann, A., Parkin, J., Fülle, J.B., Slater, P.G., Lowery, L.A., Sanchez-Soriano, N., and Prokop, A. (2021). Tau, XMAP215/Msps and Eb1 co-operate interdependently to regulate microtubule polymerisation and bundle formation in axons. PLoS Genet 17, e1009647.
- - Mahmood, I., Martinez-Hernandez, U., and Dehghani-Sanij, A.A. (2020). Evaluation of gait transitional phases using neuromechanical outputs and somatosensory inputs in an overground walk. Human Movement Science 69, 102558.
- - Ali, M.F., Fatema, U., Peng, X., Hacker, S.W., Maruyama, D., Sun, M.-X., and Kawashima, T. (2020). ARP2/3-independent WAVE/SCAR pathway and class XI myosin control sperm nuclear migration in flowering plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 32757–32763. 10.1073/pnas.2015550117.
- - Yu, S., Steuer Costa, W., Liewald, J.F., Shao, J., and Gottschalk, A. (2019). Synapsin is required for dense core vesicle capture and cAMP-dependent neuropeptide release (Neuroscience).
- - Galiana, E., Cohen, C., Thomen, P., Etienne, C., and Noblin, X. (2019). Guidance of zoospores by potassium gradient sensing mediates aggregation. J. R. Soc. Interface 16, 20190367.
- - Trigo, D., Goncalves, M.B., and Corcoran, J.P.T. (2019). The regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in neurite outgrowth by retinoic acid receptor β signaling. The FASEB Journal 33, 7225–7235.
- - Nakos, K., Rosenberg, M., and Spiliotis, E.T. (2019). Regulation of microtubule plus end dynamics by septin 9. Cytoskeleton 76, 83–91.
- - H. A. Ryan, S. Hirakawa, E. Yang, C. Zhou and S. Xiao, High-Voltage, Multiphasic, Nanosecond Pulses to Modulate Cellular Responses, in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 338-350, April 2018.
- - Sawamiphak, S., Kontarakis, Z., Filosa, A., Reischauer, S., and Stainier, D.Y.R. (2017). Transient cardiomyocyte fusion regulates cardiac development in zebrafish. Nature Communications 8.
- - Breznau, E.B., Murt, M., Blasius, T.L., Verhey, K.J., and Miller, A.L. (2017). The MgcRacGAP SxIP motif tethers Centralspindlin to microtubule plus ends in Xenopus laevis. Journal of Cell Science 130, 1809–1821.
- - Elaina B. Breznau (2016). Regulation of epithelial cytokinesis and cell-cell junctions by MgcRacGAP. University of Michigan.
- - Monteith, C.E., Brunner, M.E., Djagaeva, I., Bielecki, A.M., Deutsch, J.M., and Saxton, W.M. (2016). A Mechanism for Cytoplasmic Streaming: Kinesin-Driven Alignment of Microtubules and Fast Fluid Flows. Biophysical Journal 110, 2053–2065.